
Celecoxib versus Diclofenac and Omeprazole in Reducing the Risk of Recurrent Ulcer Bleeding in Patients with Arthritis | NEJM
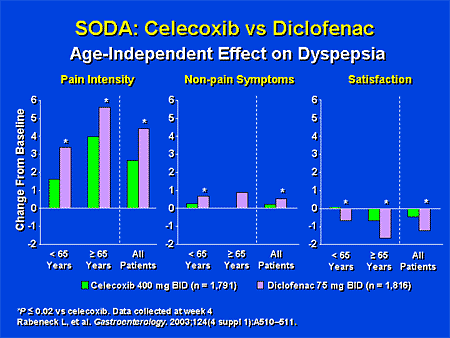
Hot Topics in Gastroenterology: Management of Nonselective NSAID-Related Toxicity Up and Down the GI Tract

Celecoxib versus diclofenac in long-term management of rheumatoid arthritis: randomised double-blind comparison - The Lancet

Lessons from 20 years with COX‐2 inhibitors: Importance of dose–response considerations and fair play in comparative trials - Stiller - 2022 - Journal of Internal Medicine - Wiley Online Library

Celecoxib versus diclofenac in long-term management of rheumatoid arthritis: randomised double-blind comparison | Semantic Scholar

Cardiorenal effects of celecoxib as compared with the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs diclofenac and ibuprofen - ScienceDirect

Celecoxib Versus Naproxen and Diclofenac in Osteoarthritis Patients: SUCCESS-I Study - ScienceDirect

Celecoxib versus omeprazole and diclofenac in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis (CONDOR): a randomised trial | Semantic Scholar

Celecoxib for arthritis relief less likely to cause gastrointestinal damage than diclofenac + omeprazole

Celecoxib versus omeprazole and diclofenac in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis (CONDOR): a randomised trial | Semantic Scholar
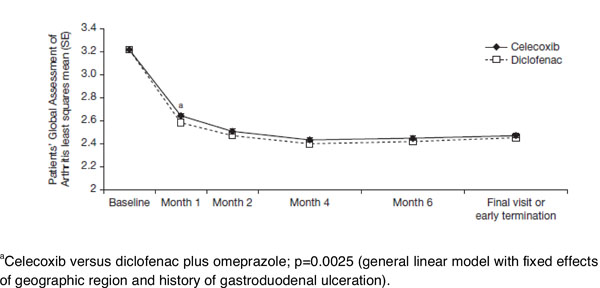
Celecoxib and Diclofenac Plus Omeprazole are Similarly Effective in the Treatment of Arthritis in Patients at High GI Risk in the CONDOR Trial

Celecoxib versus Diclofenac and Omeprazole in Reducing the Risk of Recurrent Ulcer Bleeding in Patients with Arthritis | NEJM
Nimesulide, aspirin, acetylsalicylic acid, ibuprofen, diclofenac, Indometacin, naproxen, ketoprofen, nimesulide, celecoxib molecules. It is NSAIDs. Ve Stock Vector Image & Art - Alamy

PDF) Celecoxib versus diclofenac for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: 12-week randomized study in Norwegian patients

Cardiovascular outcomes with etoricoxib and diclofenac in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis in the Multinational Etoricoxib and Diclofenac Arthritis Long-term (MEDAL) programme: a randomised comparison - The Lancet

Celecoxib versus diclofenac for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: 12-week randomized study in Norwegian patients – topic of research paper in Clinical medicine. Download scholarly article PDF and read for free on







![nsaid_side_effects [TUSOM | Pharmwiki] nsaid_side_effects [TUSOM | Pharmwiki]](https://tmedweb.tulane.edu/pharmwiki/lib/exe/fetch.php/nsaidsratio.png?w=700&tok=57e133)